Albrecht Dürer: 10 Facts To Know
-
Albrecht Dürer Facts
- 1. Dürer showed talent at an early age
Albrecht Dürer was born in Nuremberg, Germany in 1471, one of 18 children born to Albrecht and Barbara Dürer (only three of whom survived to adulthood). His father was a successful goldsmith of Hungarian heritage, and young Albrecht apprenticed with him before deciding on an artistic career instead.
Durer showed talent at an early age. The silverpoint Self-Portrait of 1484, in which he depicted himself wide-eyed and chubby-cheeked, is the earliest, securely attributed self-portrait by a European Master that survives, and was created when he had barely become a teenager.
2. Dürer’s home city was one of the most important in Europe
Lying at the heart of the Holy Roman Empire, Nuremberg was an economic and manufacturing hub. Silver and copper mined in nearby Saxony and Bohemia were transformed by the city’s myriad metalworkers into luxury and utilitarian wares. The city was also a crucible of humanist thought – reflecting on its multiple printing houses (which helped to rapidly circulate the messages of the Reformation), Martin Luther called it ‘the eyes and ears of Germany’.
There still existed in Nuremberg a gothic, medieval sensibility, something that Dürer tapped into with his fantastical woodcut series from 1498, The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse. The approaching end of the century prompted rumours about the approaching end of the world. The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse’s scenes, derived from the Revelation of St John, merely added to the prevailing, eschatological mood.

3. Dürer is credited with bringing the Renaissance to Northern Europe
Dürer travelled throughout his life, picking up inspiration and clients abroad on a regular basis. His first major trip was from 1490 to 1494, his so-called Wanderjahre (journeyman years), in which he visited Frankfurt and Basel, among other places. A brief return to Nuremberg to marry (his father having organised a wedding with Agnes Frey, a wealthy local merchant’s daughter) was followed by another trip: this time across the Alps to Venice.
It was there that Durer became fascinated by the work of Andrea Mantegna and Giovanni Bellini. In subsequent decades, Dürer gained considerable fame in Italy, where even the art historian Giorgio Vasari, notably dismissive of artists from beyond Tuscany, let alone Italy, praised his ‘beautiful fantasies and inventions’.
4. Dürer was a fine painter, and an even finer printmaker
Dürer’s painted oeuvre is dominated by portraits, altarpieces and private, devotional imagery. (On his trip back across the Alps from Venice, he also painted a series of topographical watercolours, said by some to be the first pure landscape studies in art history.) It is, however, the pioneering woodcuts and engravings on which his artistic reputation really rests.
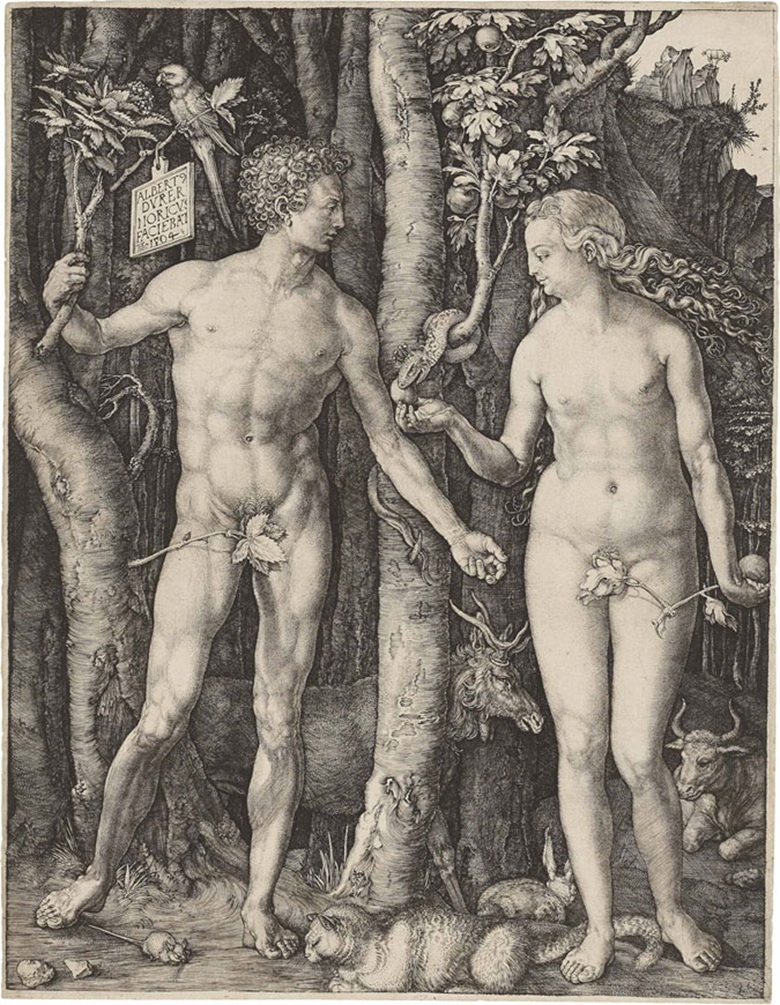
In one of his most famous, Adam and Eve, Durer captures the perfection of the world’s first couple before the Fall, showing them in idealised, near-symmetrical poses on either side of the Tree of Knowledge. The figure of Adam was inspired by the Hellenistic sculpture of Apollo Belvedere, which had recently been excavated near Rome (in 1489). Dürer brought unprecedented detail and subtlety of line to the medium of engraving, as witnessed best of all here in the human skin and tree bark.

5. Between 1513 and 1514, Dürer produced the three engravings known as his Master Prints
In a period of around 12 months, Dürer created his trio of so-called Meisterstiche (master prints), comprising three solitary figures in highly symbolic environments: St Jerome in His Study, depicting the saint peacefully at work; Melencolia I, in which the winged personification of Melancholy sits dejectedly, head in hand; and Knight, Death and the Devil I, featuring a Christian knight riding through the depths of a German forest.

In this final image, the subject is confronted by the nightmarish sight of Death and a goat-faced devil, but keeps calm and carries on, firmly gripping his reins and ensuring his horse’s steady path. Knight, Death and the Devil was adored by Adolf Hitler on the grounds that it celebrated a brave Teutonic hero, however, the horse was actually inspired by Leonardo da Vinci’s designs for the equestrian monument to Francesco Sforza in Milan.

6. Dürer was the favourite artist of the Holy Roman Emperor
In 1509, as a sign of his growing social status, Dürer was appointed to the Great Council of Nuremberg when he was in his late thirties. He also became court painter to Maximilian I in around 1512. The Holy Roman Emperor hoped to earn himself a reputation as a discerning patron of the arts, and to preserve his memory for posterity.
Realising the mass medium of the woodcut would enable him to achieve both, he commissioned Dürer to complete the monumental Triumphal Arch, for display across his empire. It is comprised of various scenes glorifying Maximilian’s military feats. With a surface area of 10 square metres, it is one of the largest woodcuts ever made.
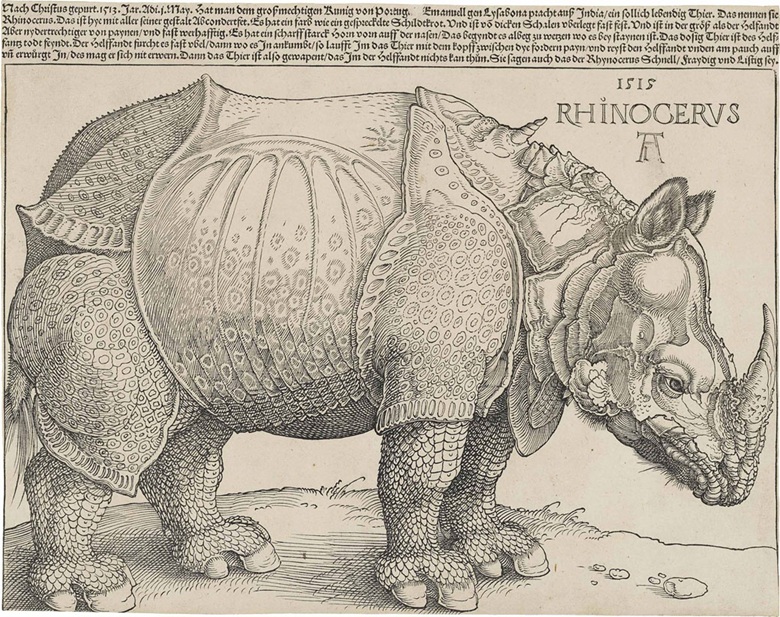
7. Dürer’s depiction of a rhinoceros is one of the most celebrated animals in art history
Dürer was alive at the time Hernán Cortés and his conquistadors were claiming the New World for Spain. The exotic booty they brought back to King Charles V (weapons, jewellery, textiles and much else besides) was the talk of all Europe. Dürer saw a selection of Meso-American treasures on a trip to Brussels in August 1520. According to an entry in his travel diary, he had ‘not seen anything in [his] whole life that delighted [his] heart as much as these… marvellously artistic things’.
It was around this time that Portuguese adventurers caused an even greater sensation by transporting a rhinoceros to Europe from India for their king, Manuel I. Dürer never saw the animal himself, but cashed in on the furore about it, producing a woodcut image of the rhino, based on a sketch by a German merchant in Lisbon. Dürer’s version came with numerous fanciful additions, intended to fire the viewer’s imagination, including folds of skin that looked like armour.
8. Dürer had one of the most famous signatures in art
Dürer was keenly aware of what today we’d call his own branding. In the mid-1490s, he started signing his works with his initials. Indeed, the ‘AD’ monogram became so esteemed and valuable that it was routinely forged by artists copying his work. Dürer even took one of these, Bologna’s Marcantonio Raimondi, to court, prompting the first copyright action in art history.
9. Dürer was an author as well as an artist
In his final years, Albrecht Dürer spent more and more time writing books about art instead of creating it. Ever since his first trip to Italy he had been a champion of what one might call a ‘Renaissance aesthetic’, determined by divine harmony and proportion. (It has even been suggested that his second trip to Italy, in 1505, was inspired by a desire to learn the secrets of Venetian artist Jacopo de’ Barbari, who’d reportedly discovered a system of ideal measurements and proportions.)
In his first book, Instructions for Measuring with a Compass and Ruler (1525), Dürer considered at length the matter of perspective. He believed that art wasn’t a humble craft, but a lofty achievement built on theoretical foundations.
10. Dürer was as feted in death as he was in life
Dürer picked up an illness (perhaps chronic malaria) on a trip to the Netherlands in 1521. From then on, bouts of fever became as regular a part of his life as consultations with a doctor. He died, aged 56, in 1528. His friend Pirckheimer penned for him the tombstone epitaph, ‘What was mortal of Albrecht Dürer lies beneath this mound’.
Other friends are said to have secretly exhumed his body a few days after its burial to make plaster casts of his face and hands. A lock of hair was also cut from his head while he lay on his deathbed and sent to Strasbourg, to his former pupil Hans Baldung. The lock is now kept in a silver-bound reliquary, in the Vienna Academy of Art.
Albrecht Durer Prints
Browse available Albrecht Durer prints from leading galleries and art dealers.
